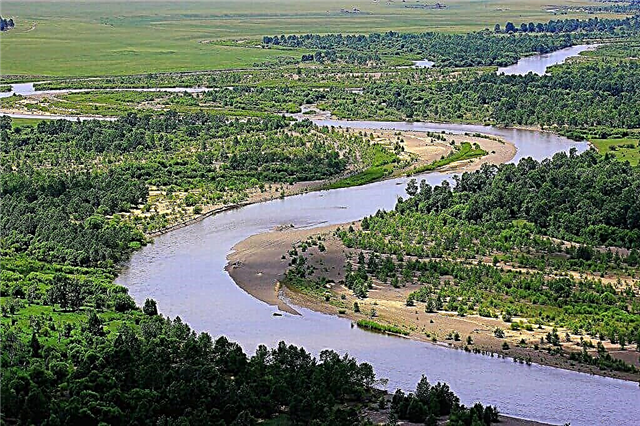
The Trans-Baikal Territory is famous for its natural beauty. More than 40 thousand streams are among the rivers flowing through this amazing region. Most of the rivers are up to 25 km long. More than 10 rivers in this territory are endowed with a length of over 500 km.
Many waterways are related to the vast basin of the Amur River. The Trans-Baikal Territory borders on the majestic Lake Baikal. Transbaikal rivers are full of fish and mammals. Otters, seals, seals and perches are typical representatives of the Trans-Baikal fauna. The water arteries of the edge have a predominant rain-fed type. Only 10% of them feed on additional food due to the melting of glaciers.
The longest rivers of the Trans-Baikal Territory
List of the region's largest waterways.
Vitim
The water artery is one of the largest rivers in Siberia. The basin area is 225 thousand km². The current forms the right tributary of the Lena. The source is located at the confluence of Vitimkan and China. It flows through the Vitim plateau. The type of food is rain-fed. The river is navigable for 500 km. Today Vitim is used for timber rafting. A large number of settlements are located on the banks of Vitim. Sports tourism is represented by rafting and kayaking. The Vitim channel has an extensive network of rapids.
The length of the river is 1837 km, in the Trans-Baikal Territory - 750 km.

Argun
Border river between China and Russia. The basin area is 164 thousand km². The source of the Argun is lost in the mountains of the Greater Khingan. It flows into the Amur. The river is fed by rain. The waterway is rich in commercial fish: carp, chum perch. Partly navigable, hidden under a thick layer of ice from November to May. The ecology of the river is in poor condition, as Chinese industries pour waste into its waters.
The length of the river is 1620 km, in the Trans-Baikal Territory - 951 km.

Olekma
The right tributary of the Lena originates in the Muroy Range. The area is 210 thousand km². There are several thermal springs at the mouth of the tributary. Olekma is prone to summer floods, it is replenished by rain and snow melting. The waterway is actively used for boating. The river bed passes through the Olekminsky reserve, where water excursions and sports competitions on the water are held.
The length of the river is 1436 km, in the Trans-Baikal Territory - 625 km.

Onon
The waterway flows through the lands of Mongolia and Transbaikalia. The area is 96 thousand km². The source of Onon is in the Hentei Highlands. The river flows into the Amur basin. It feeds on snowy waters. Onon is used in irrigation of crops and for industrial purposes. According to an old legend, Genghis Khan was born in the upper reaches of this particular river in Mongolia.
The length of the river is 1032 km, in the Trans-Baikal Territory - 734 km.

Chara
The river connects the Trans-Baikal Territory, Buryatia and the Irkutsk Region. The water area is 87 thousand km². Chara flows into Olekma. More than 7 thousand lakes can be counted in the basin of the waterway. The source is located on the Udokan ridge. The river forms rapids near the Kodar. The mountainous shores of Chara are densely overgrown with forest. On the left bank of the char, there is a rare charoite deposit. Sports rafting is carried out on the river. The lower reaches of the Chara are considered navigable areas.
The length of the river is 851 km, in the Trans-Baikal Territory - 410 km

Khilok
The river is a link between Buryatia and Transbaikalia. The basin area is 38 thousand km². The source is located at Lake Arakhley. It flows into the Selenga. The river is fed by summer and autumn rains. The banks of the waterway are densely populated. The lower reaches of the river are used for navigation and timber rafting. There are few rapids on the river.
The length of the river is 840 km, in the Trans-Baikal Territory - 670 km.

Chikoy
The Selenga tributary originates from the Chikokonsky ridge. The area is 46 thousand km². The river connects Transbaikalia, Buryatia and Mongolia with its channel. There are many branches and islands in the lower reaches of the Chikoi. The rain type of feeding leads to summer floods. The Yamarovka resort operates in the upper reaches of the river. The Chikoya navigable section is 152 km. The water area is partially used for irrigation, and also for boating. There are many settlements scattered along the entire river bed.
The length of the river is 769 km, in the Trans-Baikal Territory - 500 km.
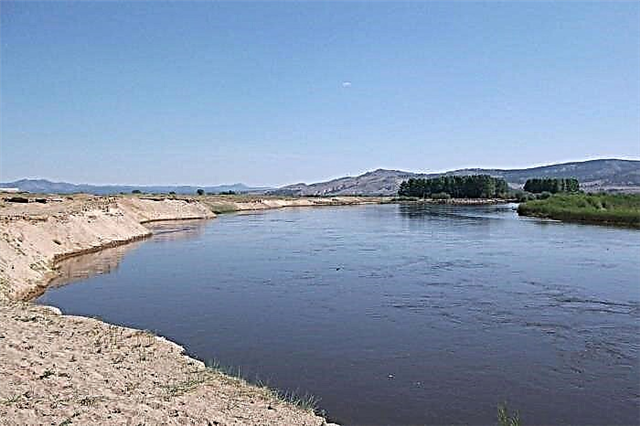

Ingoda
The beginning of the river is worth looking for in the depths of the Khentei mountain range. The area is 37 thousand km². Fishing is carried out on the river. Minnow, chebak, catfish, burbot have chosen these waters for breeding. The fauna of Ingoda also includes rare crayfish. The river flows into the Amur. The water level is maintained here by rains and small tributaries.
The length of the river is 708 km.

Gazimur
The left tributary of the Argun river begins in the west of the Nerchinsky ridge. The basin area is 12 thousand km². The steep banks of the river are almost completely covered with low-growing bushes. After the ice melts in May during the summer, Gazimur becomes shallow, because of this, many fords are formed in the channel. The population density of the banks of Gazimur is average.
The length of the river is 592 km.

Nercha
The left tributary of the Shilka flows to the plains from the Yablonovy ridge. The basin area is 27 thousand km². The city of Nerchinsk is located by the river. The river bed is meandering and heterogeneous. Water tourism is developed in large settlements on Nerch. Mixed forests grow along the river banks.
The length of the river is 580 km.

Shilka
The left tributary of the Amur is born due to the confluence of Onon and Ingoda. The area is 206 thousand km². The river bed occupies the valley between the Shilkinsky and Amazar ranges. Rapids, waterfalls, boulders - this is what the Shilka relief consists of. The shallow river is navigable downstream. Deposits of gold and non-ferrous metals were found in the Shilka water basin. The Shilkinskaya HPP is located and operates on Shilka.
The length of the river is 560 km.

Kalar
The right tributary of the Vitim flows out of the Stanovoye Upland. The basin area is 17 thousand km². The nature of the Kalara coastal zone is rich in larch, cedar, pine and fir. Food - rain. Tourists and sportsmen float down Kalar on rafts, kayaks, boats and rafts. The rapids here have 4 categories of difficulty. Taimen, grayling, whitefish are found in the waters of Kalar. There is the village of Sredny Kalar on the river.
The length of the river is 511 km.

Tungir
The river flows along the Gulsky ridge. It is a tributary of the Olekma. The water area is 14 thousand km². The source can be found on the slope of the Tungir ridge. The channel stretches along a spacious intermountain valley. The type of food is mixed: rain and snow. The river is frozen from October to May. Tungir is well suited for tourism and boat trips.
The length of the river is 500 km.

Karenga
The right tributary of the Vitim is fed by rainwater. The area is 10 thousand km². The source is based at the Yablonovy ridge. The Karenga bed passes through the intermontane basin. On the slopes of the river channel, archaeologists discovered household items of the first people of the Neolithic era. In the warm months of the year, the water level in Karenga rises sharply. The river is under the ice from October to April.
The length of the river is 366 km.

Menza
The river system covers the lands of Russia and Mongolia. The basin area is 13 thousand km². The source is located on the slope of the Baga-Khentei ridge. Commercial fish species are found in Menza: taimen, perch, burbot, catfish. Ancient burials were found at the confluence of the Menza and Chikoy. The river freezes over from November to April, and becomes full-flowing in summer.
The length of the river is 337 km, in the Trans-Baikal Territory - 200 km.

Kalakan
The water artery is the right tributary of the Vitim. The basin area is 10 thousand km². The source is located in the west of the Vitim plateau. The channel runs along the southern side of the Yankan ridge. Type of food - rain and snow. The river bed abounds in a large number of rapids. Almost along the entire length of the river there are navigable and rafting sections. The forests around are rich in game, mushrooms and berries.
The length of the river is 314 km.

Amazar
The left tributary of the Amur is formed by the confluence of the Big and Small Amazar. The channel runs along the Amazar ridge. The water area is 11 thousand km². There are 104 small lakes in the Amazar basin.Type of food - rain, floods occur in summer. Partially near settlements, the river is suitable for rafting. Since 1858, the village of Amazar has been growing and developing on the river.
The length of the river is 290 km.

Level
The water artery is a tributary of the Argun. The basin area is 4 thousand km². The source is located in a lake on the slope of the Nerchinsky ridge. The river bed is winding, hidden under the ice from October to May. The relief of the area where Urov flows includes the Urov depression. The river is endowed with rapids and deep calm areas. Wild tourism is developed in these places.
The length of the river is 290 km.

Unda
The tributary of the Onon River begins at the spurs of the Kukulbei mountain range. The water area is 9 thousand km². The Unda has 130 tributaries. There are 289 lakes in the water area. A large city on the banks of the Unda is Baley. Some parts of the river system are suitable for boat navigation. In winter, the waterway almost completely freezes over, in summer floods occur on Unda due to frequent rains.
The length of the river is 273 km.

Olengui
The river is considered a tributary of the Ingoda. The area is 4 thousand km². The source is located near the Daursky ridge. Olengui has several tributaries. The river opens up in May; in summer, the water level in it is full-flowing without shoals. The river bed is relatively straight, there are few rapids. The banks of the Olengui are sparsely populated.
The length of the river is 214 km.

Chitinka
The river artery flows into the Ingoda. The location of the source is indicated at the Chersky ridge. The channel runs through the territory of the Chita region. The confluence with the Ingoda occurs near the city of Chita. In recent years, the ecological state of the river has deteriorated. The channel has become shallow, the waters are considered contaminated with industrial waste. The situation with Chitinka is complicated by illegal withdrawal of sand and gravel mixture from the channel. The river needs urgent restoration measures.
The length of the river is 210 km.

Kuanda
The right tributary of Vitim originates in the waters of Lake Leprindokan. The basin area is 6 thousand km². The river system has several tributaries. The banks of the river are rich in mixed forest. Larch, cedar, fir grow there, as well as various types of pine. There is a large village of the same name on the river. The area of the river and the village is subject to the threat of forest fires. The river bed is quite straight and deep. The type of food is rain-fed.
The length of the river is 196 km.

Ungo
The left tributary Khilka is famous for its fishing spots. The water area is 2 thousand km². Lenok, grayling, perch and catfish are found everywhere in Ungo. The banks of the river system are covered with dense forests. The water in Ungo is clean and clear, in some places the bottom is clearly visible.
The length of the river is 189 km.

Cuenga
The river area is a tributary of the Shilka. The source of the river is lost somewhere in the Nerchinsk mountains. The area is 7 thousand km². Cuenga is opened by the end of April. Floods are possible on the river in spring and autumn. It is noteworthy that the thickness of the ice on the river in winter is 200 cm. Tourism on Kuenga is represented by water excursions and fishing tours.
The length of the river is 170 km.

Turga
The right tributary of the Onon has its source in the bowels of the Onon mountain range. The basin area is 3 thousand km². The upper reaches of the river dry up during the dry season. In winter, Turga completely freezes over. There are several settlements on the banks of the river, one of them is called the river. The Turgi channel has several rapids where tourist rafting is possible. The nature around Turga is endowed with all the Trans-Baikal virtues: mixed forest, diverse fauna and flora. The river itself is a great fishing spot.
The length of the river is 168 km.